I’m thrilled and privileged to have become part of the DiverseNile team in November 2023. My primary role entails consolidating and organizing the data on the variability of funerary monuments excavated in the Attab to Ferka region of Northern Sudan during the 2022 and 2023 seasons. Our PI Julia Budka has given me the specific task of preparing the documentation of Feature 50 from Trench 5 in the Kerma cemetery GiE 003 (see Budka 2022). Interestingly, this burial shows many features associated with the Pan-Grave culture.

The filling of Feature 50 comprised a diverse array of artifacts (see Budka, Rose, Ward 2023, 34), including pottery sherds, bones of at least one individual and three goats, beads, remnants of a wooden bed, alongside a mix of dense clay or mud fragments. The latter might have constituted a section of the superstructure wall surrounding the burial (cf. Irish 2007, 59, Figs. 2-3). Due to their dispersed nature within the tomb, not all of these finds were unearthed together or found within a single layer, necessitating their documentation either partially or separately.
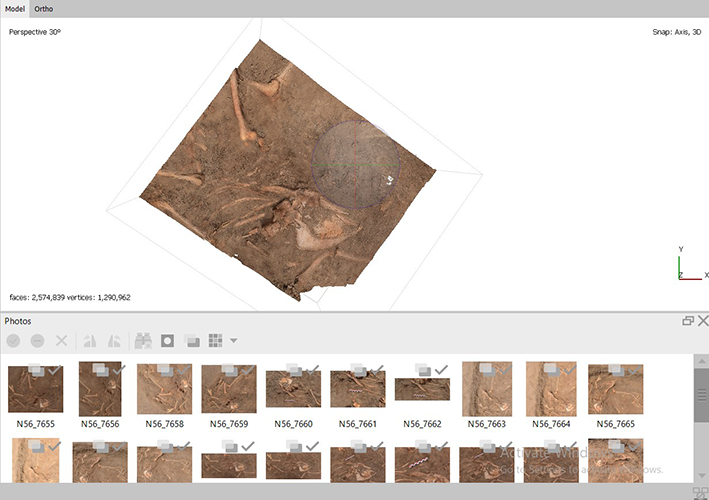
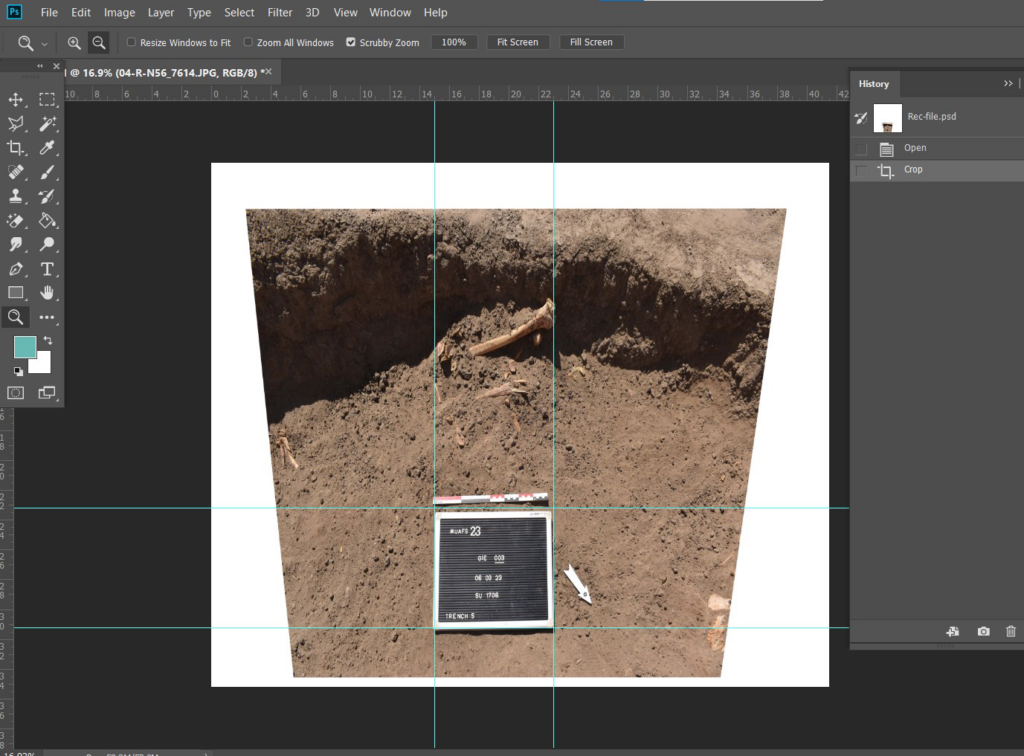
Because different parts of the same level were documented separately, I endeavored to amalgamate all these disparate 3D models into one comprehensive representation using Adobe Illustrator. This involved consolidating all the finds in a unified layout. Additionally, I utilized site photos, rectified them through programs like Metashape or Photoshop, and incorporated them into the combined models.
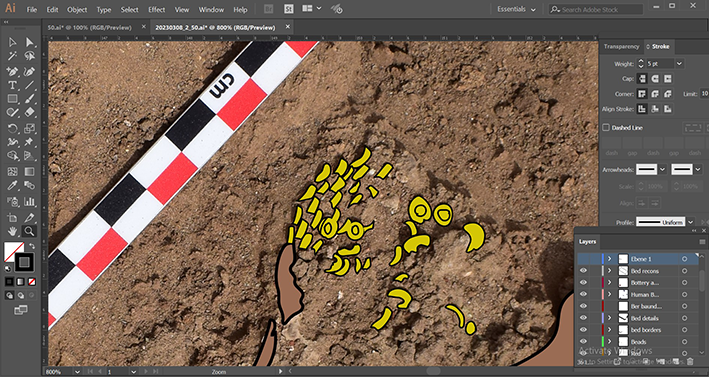
I also leveraged daily site information, occasionally using the models as close-ups for finer details. Furthermore, throughout this process, I engaged in numerous discussions with Julia to ensure accuracy and completeness.
In the end, through our collaborative efforts, we successfully integrated all elements into a single cohesive representation, meticulously illustrated using Adobe Illustrator.

The clarity of having everything consolidated sparked the idea of creating a reconstruction view using Adobe Illustrator. Inspired by this, I began exploring parallel cemeteries associated with the Pan-Grave horizon, including C-group burials (which are a bit earlier but nevertheless useful parallels). To enhance the visualization, I utilized Photoshop to craft different positions for the goat skeletons. However, despite these efforts, the original view remained somewhat unclear. This led me to consider creating a 3D model reconstruction using Google Sketch-Up, providing a clearer representation of all the features and finds.
Finally, I managed to develop a preliminary 3D reconstruction, but further investigation is needed. Interestingly, Pan-Grave burials, contrasting to Kerma burials, normally do not have wooden funerary beds.
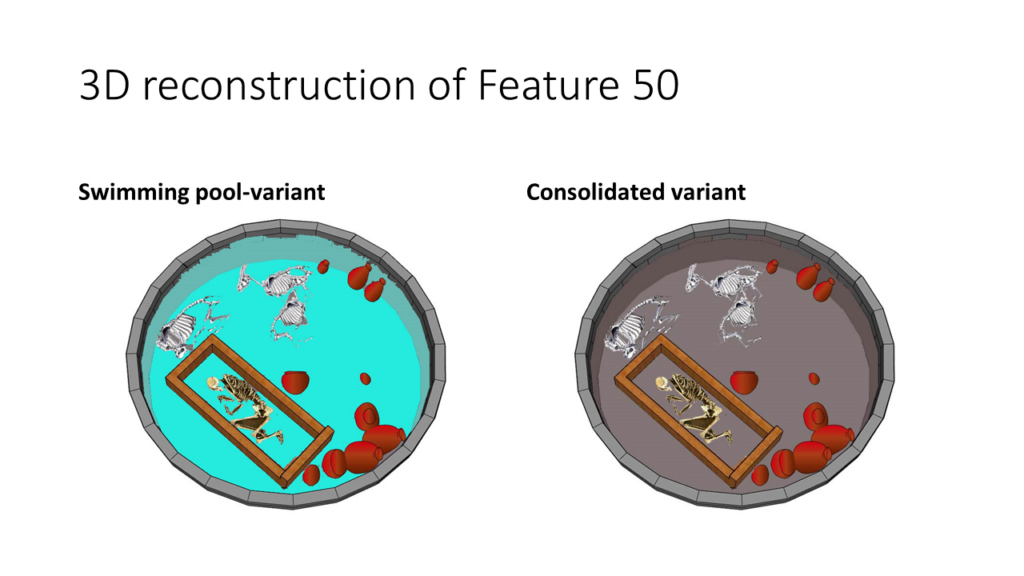
One last aspect: It’s incredible how something as simple as a color choice can drastically alter the way we perceive a scene. Chloe’s observation about the light blue floor of my reconstruction resembling a swimming pool was certainly amusing, but it prompted a smart adjustment to a grayish color to avoid any unintended connotations. These lighthearted moments amidst the serious work of archaeological reconstruction bring a sense of fun and camaraderie to the team.
References
Budka 2022 = Budka, J., Investigating Nubian funerary practices of marginal communities: new evidence from a Kerma cemetery at Ginis, Egitto e Vicino Oriente 45 (2022), 37‒62.
Budka, Rose & Ward 2023 = Budka, J., Rose, K. & C. Ward, Cultural diversity in the Bronze Age in the Attab to Ferka region: new results based on excavations in 2023, MittSAG – Der Antike Sudan 34 (2023), 19−35.
Irish 2007 = Irish, J.D., Overview of the Hierakonpolis C-Group dental remains, Sudan & Nubia 11 (2007), 57-72.
