My personal favorite landscape in the MUAFS concession area is the left riverbank of the districts Ginis and Kosha which is also rich in archaeology. Beautiful sand dunes and tamarisks dominate the strip along the Nile; desert and rocky outcrops shape the hinterland.
Despite of Covid-19 and the unclear situation regarding our next field season in Sudan, we are of course planning for the ERC DiverseNile project. One of the main tasks for the next season will be test excavations at habitation sites at Kosha West.
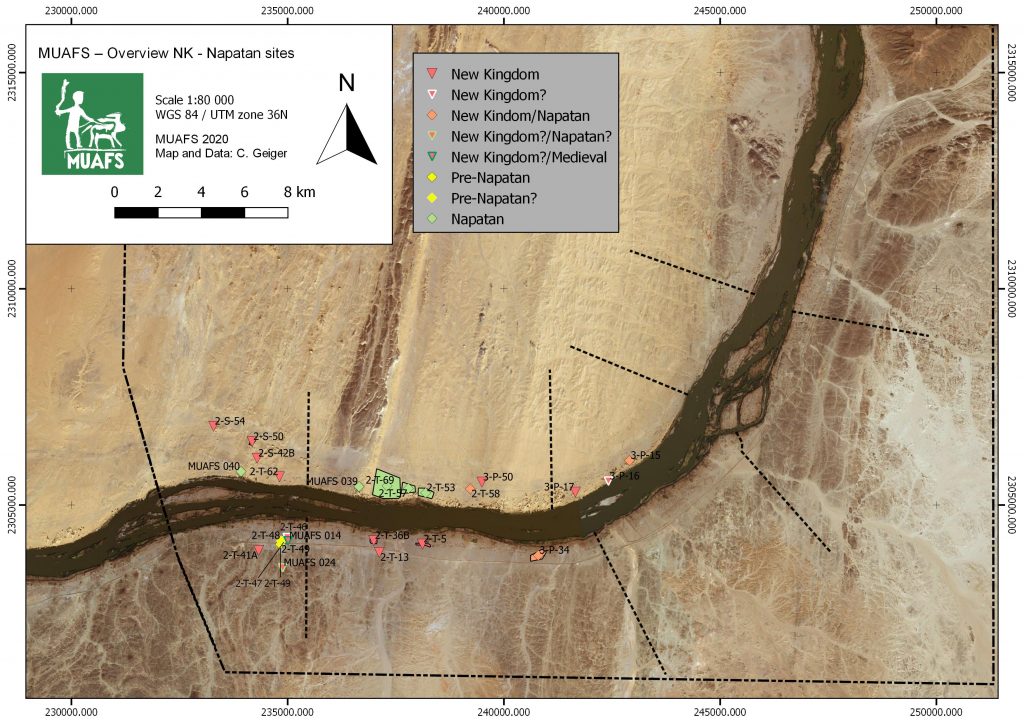
If one looks at our new distribution map of sites dating to the New Kingdom, Pre-Napatan and Napatan times, it is striking that the most downstream ones are three sites in the district Kosha West.
These are remains of structures/dwellings, situated on three isolated mounds on the dune area with tamarisks. The distance to the Nile is 100-150m. This group of habitation site was already noted by André Vila in the 1970s and he attributed all of them to the Egyptian New Kingdom. This is, however, not the case.
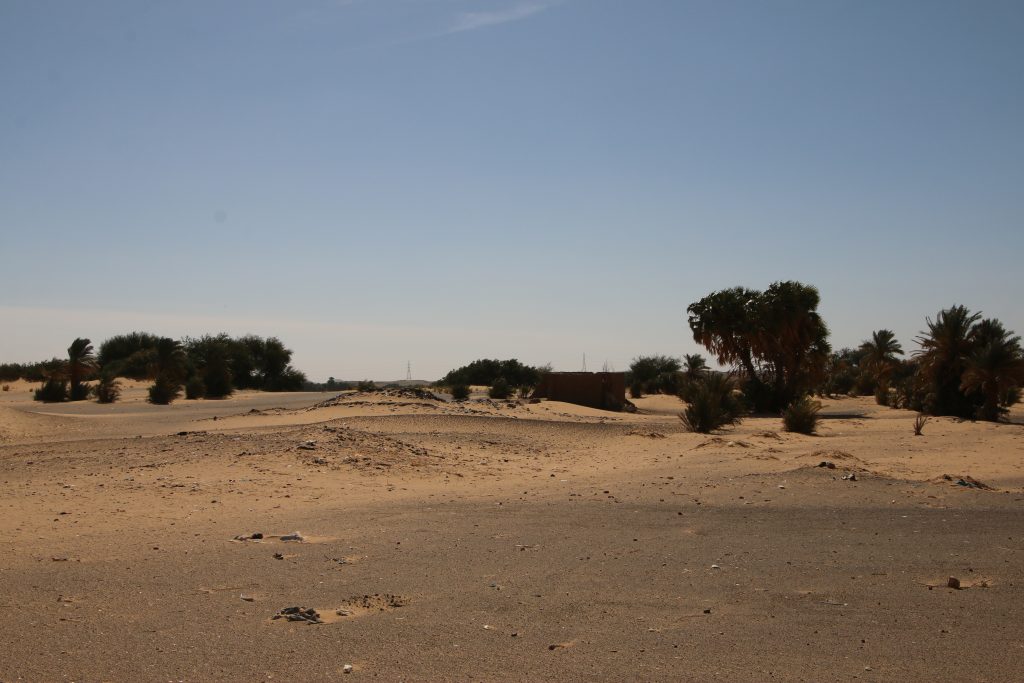

3-P-17 is traceable with some mud bricks and scattered stones on a mound, the total extension of the site is at present a bit unclear. According to the surface pottery we recorded last year, this site can be attributed to the early 18th Dynasty.
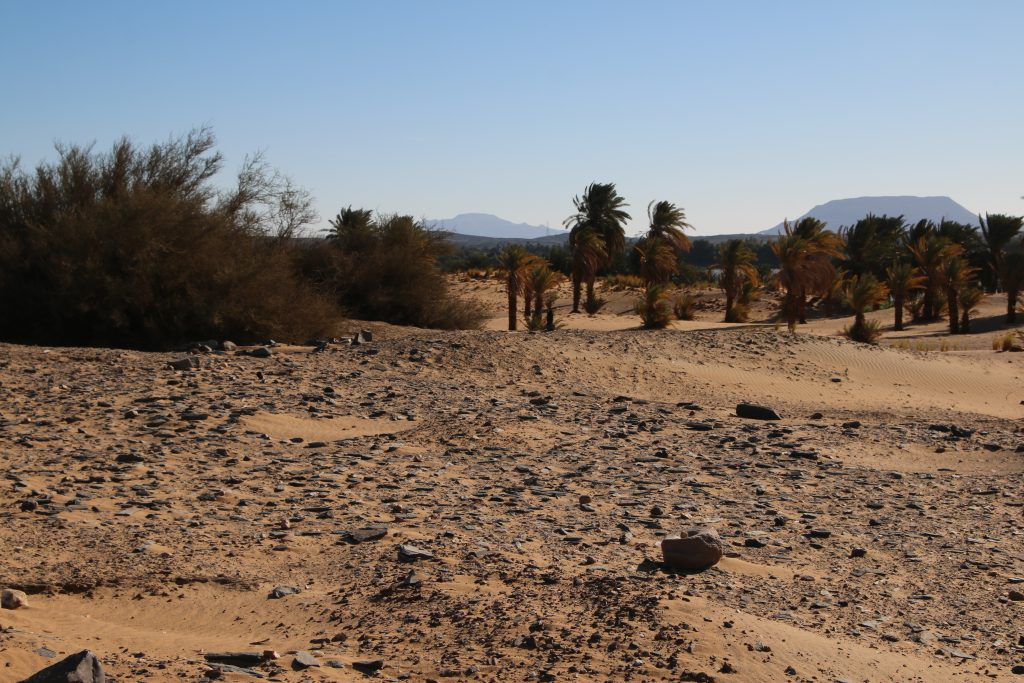
The remains of 3-P-16 are located on a circular mound with a diameter of c. 50m. In the south-eastern part of the mound large amount of mud bricks seem to have once formed a fortification. The dating of this structure must remain unclear for now; the surface material suggests indeed a New Kingdom date, but there were also some Medieval sherds.

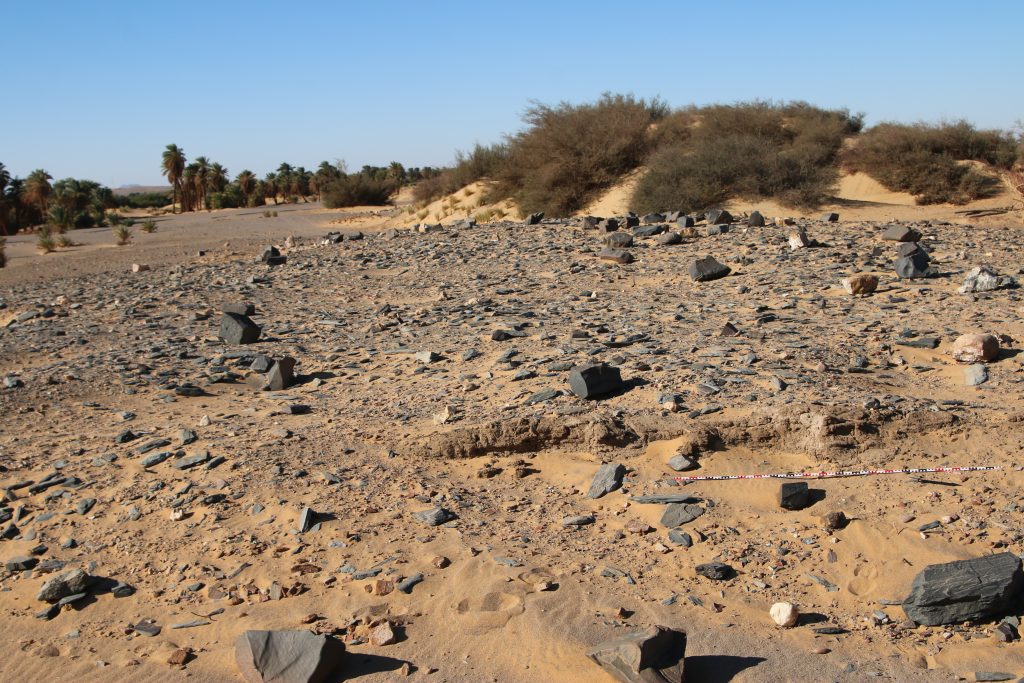
The third habitation site, 3-P-15, comprises a mound of c. 55-100m, the surface is covered by schist blocks and sherds. The appearance of the site is very similar to 3-P-16. In the northeastern part, remains of mud bricks are visible. 3-P-15 is especially intriguing because it shows a continuation from late Ramesside times well into the ninth and maybe even the eight century BC according to the surface ceramics we documented. A more precise dating and a concise characterisation will require excavations – but a New Kingdom only date as suggested by Vila seems were unlikely.

For now, we keep our fingers crossed that the Covid-19 situation in Sudan – and of course everywhere else! – will soon improve and everybody stays healthy. Insha’allah our planned fieldwork will be possible somewhen in the near future – there are definitly plenty of things to be checked and discovered between Attab and Ferka!
