With my appointment as the newest member of the DiverseNile team, it’s now time to present Work Package 2: The Variability of Funerary Monuments in the Region from Attab to Ferka, Northern Sudan.
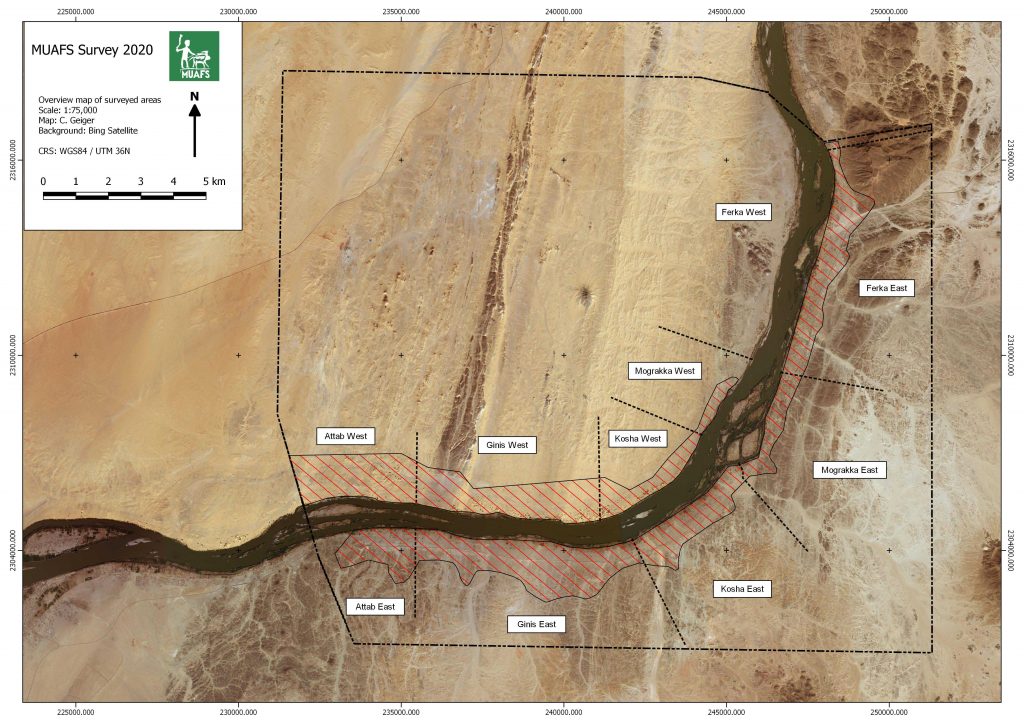
As responsible for Work Package 2, I will investigate, with PI Julia Budka, all aspects of mortuary sites within the MUAFS concession area (figure 1). The area from Attab to Ferka was firstly surveyed by André Vila within a larger survey from Dal to Missiminia. The results of Vila’s survey were published by the French CNRS in 15 volumes, which describe numerous sites located in the area. Volumes 3 to 6 focus on the MUAFS concession in the region from Attab to Ferka.
Vila identified a series of funerary sites between Attab and Ferka, which I will explore in my research within the DiverseNile team. The aim is to understand the materialisation of cultural diversity through tomb architecture, burial customs and goods, focusing on the Bronze Age, which in our concession area comprises the Kerma, Egyptian New Kingdom and Napatan periods.
The 2018/19 and 2020 seasons of MUAFS survey re-identified and documented various burials sites previously listed by Vila, some of which were extensively plundered in recent times (Budka 2019; see also our online reports). Two cemeteries at Ginis East seem to be especially relevant for future excavation. GiE002 (Vila site 2-T-13) and GiE003 (Vila site 2-T-13) date to the Kerma Period and Egyptian New Kingdom, respectively. Kerma cemeteries usually comprise tumuli burials, while New Kingdom sites include shaft tombs with no preserved superstructure. Magnetometry was carried out at both sites in 2019 and will be used to further assess the archaeological potential of the cemeteries to plan future excavations. An additional survey is also planned for the next season, which will hopefully reveal more potentially relevant cemeteries or isolated tombs.
Besides new excavations, a large part of research on mortuary sites in our concession area consists of revisiting publications, archives and material culture previously excavated and now in museums. I’m currently developing a research strategy that will explore both avenues. My PhD experience demonstrated the huge potential of revisiting old excavation reports and archival material (see, for example, Edwards 2020), as well as museum collections from a fresh theoretical perspective.
In general, the DiverseNile project focuses on shifting conceptualisations and experiences of ‘centres’ and ‘peripheries’. My previous research stresses the contextual role performed by foreign objects in local contexts in New Kingdom cemeteries in Nubia. I argue that foreign, Egyptian-style objects could perform alternative, local tasks other than materialising Egyptian colonisation through objects in Nubian contexts (Lemos 2020). DiverseNile Work Package 2 will combine both general theoretical perspectives to unveil cultural diversity in contexts previously thought to express homogenisation only.
I am also particularly interested in refining our understanding of New Kingdom chronology in Nubia. So far, Egyptocentric approaches have mainly accepted that the same dates used to understand Egyptian history apply to Nubian colonial contexts. In my PhD thesis, I discuss the use of alternative terminology, based on local Nubian experiences of colonisation, instead of landmarks of Egyptian political history. DiverseNile has been adopting ‘Bronze Age Nubia’ as a working alternative. PI Julia Budka and I will be closely working on this topic, and I hope that new excavations will provide us with more refined dates than those usually extracted from typological approaches to sites and material culture. This would be especially relevant for the end of the New Kingdom colonial period/pre-Napatan Period, which is still poorly understood (e.g., Thill 2007; Binder 2011).
Stay tuned to this space for updates regarding my work on mortuary sites and material culture in Attab-Ferka!
References
Binder, M. 2011. The 10th-9th century BC – New Evidence from Cemetery C of Amara West. Sudan & Nubia 15: 39-53.
Budka, J. 2019 (with contributions by G. D’Ercole, C. Geiger, V. Hinterhuber and M. Scheiblecker). Towards Middle Nile Biographies: the Munich University Attab to Ferka Survey Project 2018/2019. Sudan & Nubia 23: 13-26.
Edwards, D. ed. 2020. The Archaeological Survey of Sudanese Nubia, 1963-1969. The Pharaonic Sites. Oxford: Archaeopress.
Lemos, R. 2020. Material Culture and Colonization in Ancient Nubia: Evidence from the New Kingdom Cemeteries. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology, ed. C. Smith. New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51726-1_3307-1
Thill, F. 2007. Les réoccupations “(pré)napatéennes” dans le cimetière égyptien 8B5/SAC5 de Sai. In Mélanges offerts à Francis Geus, ed. B. Gratien. CRIPEL 26: 353–369.
