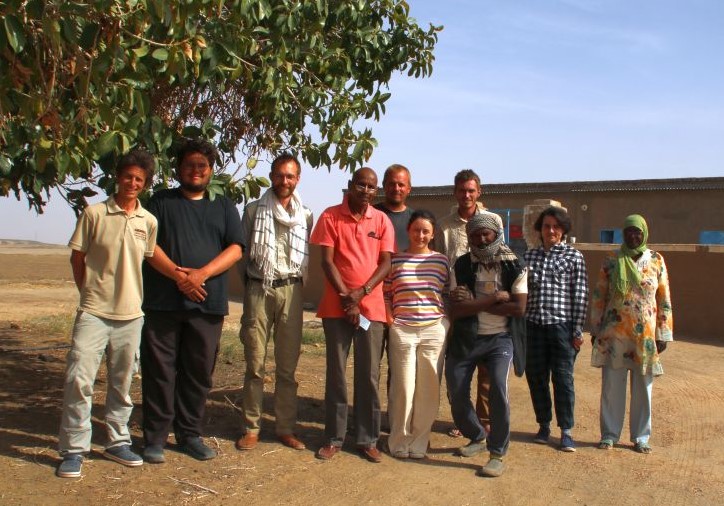
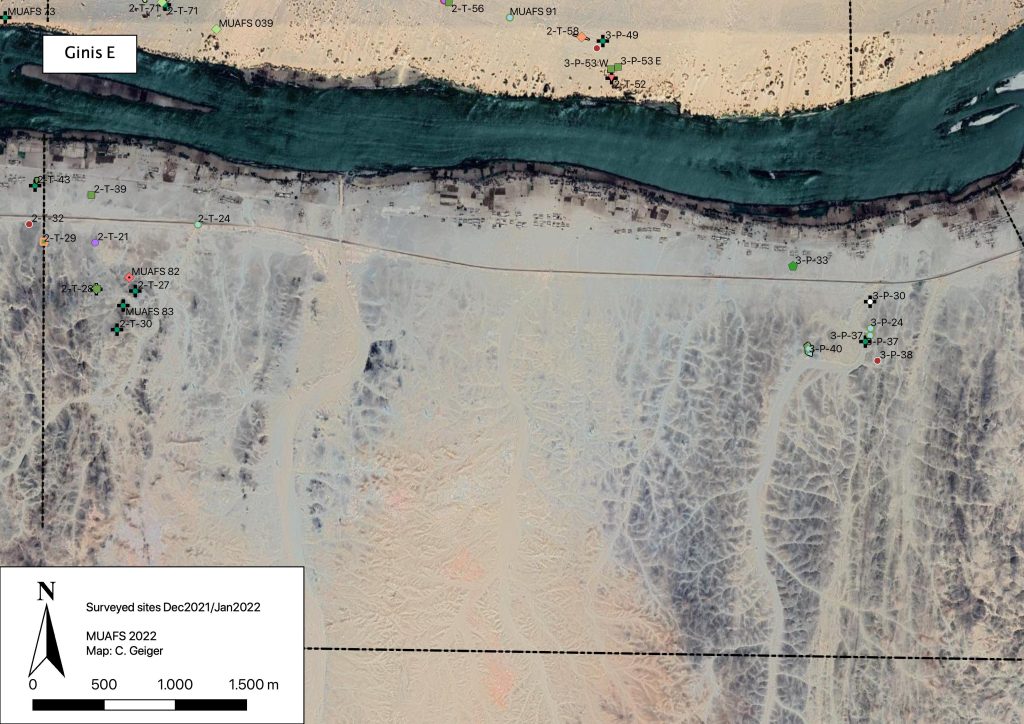
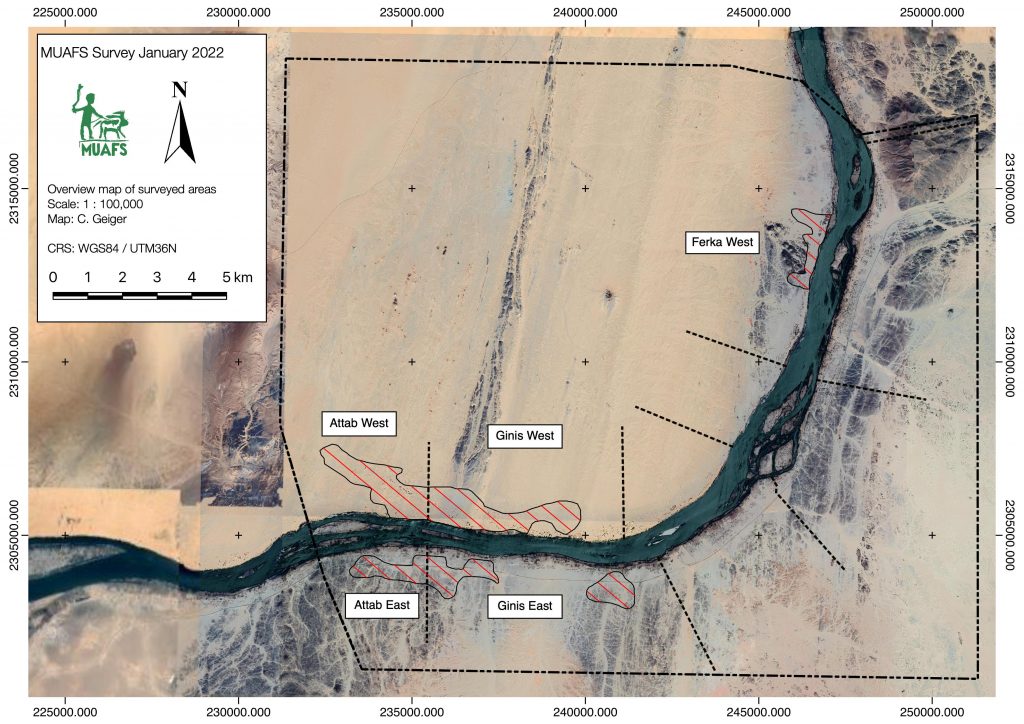
The 15th International Conference for Nubian Studies in Warsaw is approaching at the end of this month, and I am currently busy preparing my paper. I will give a brief overview of the main results of the MUAFS project in the past years – and thus I revisited some of the sites of major interest between Attab and Ferka.
Until now, our work only focused on the left and right banks of the Nile – but my concession also comprises all the islands of the region. While we still have to visit Firkinarti island close to Ferka with its impressive archaeological remains, Huda and I spent one productive day this January on Gergetti island during our survey season.
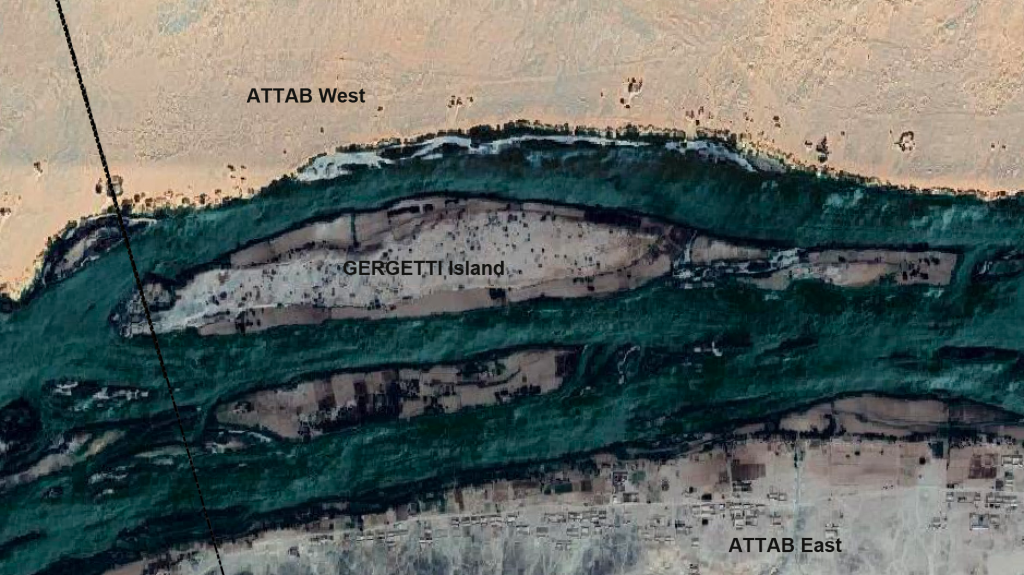

Gergetti island is a beautiful island dominated by sandy dunes, located between Attab East and Attab West with an East West extension of c. 1.7km and a North South extension of c. 250m. The landscape and the view to the east bank is stunning – and provides a completely different view of Gebel Abri than I was used to when working on Sai island.
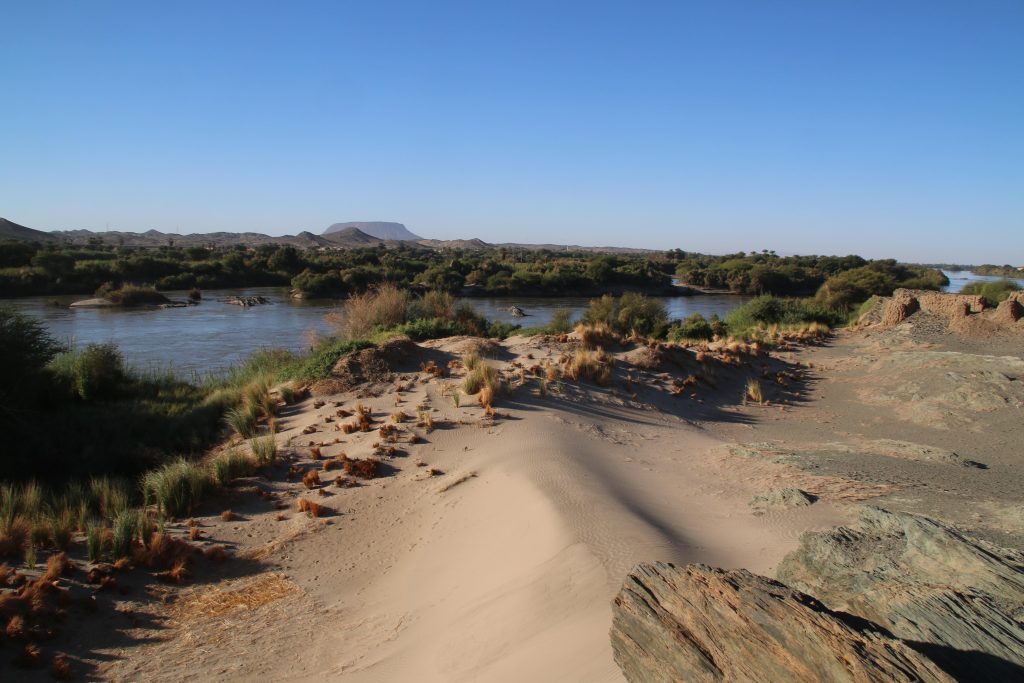

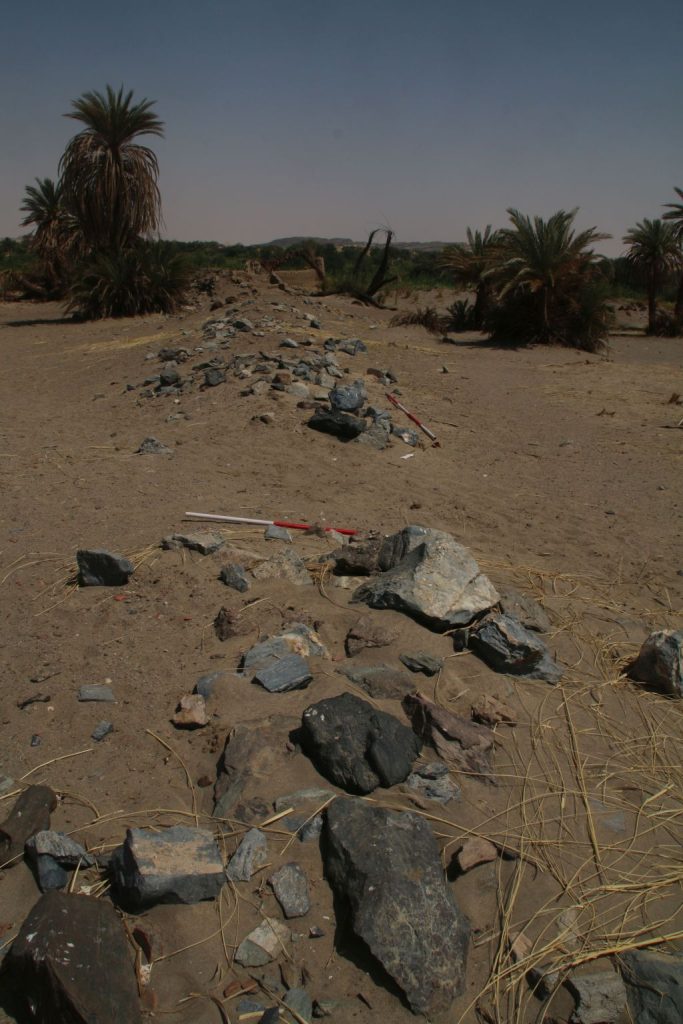
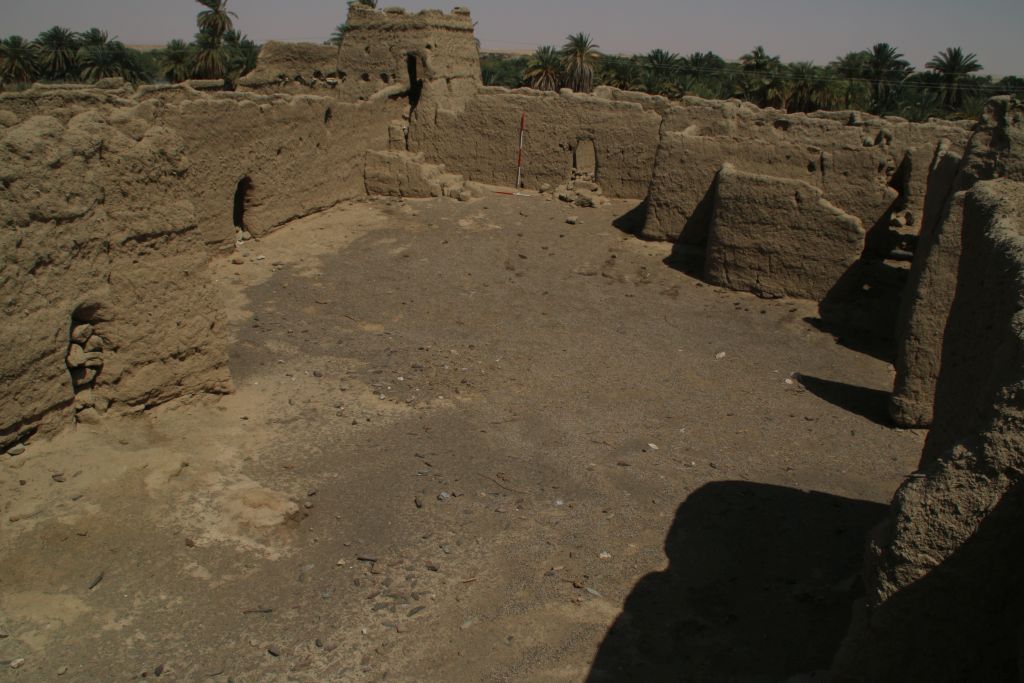
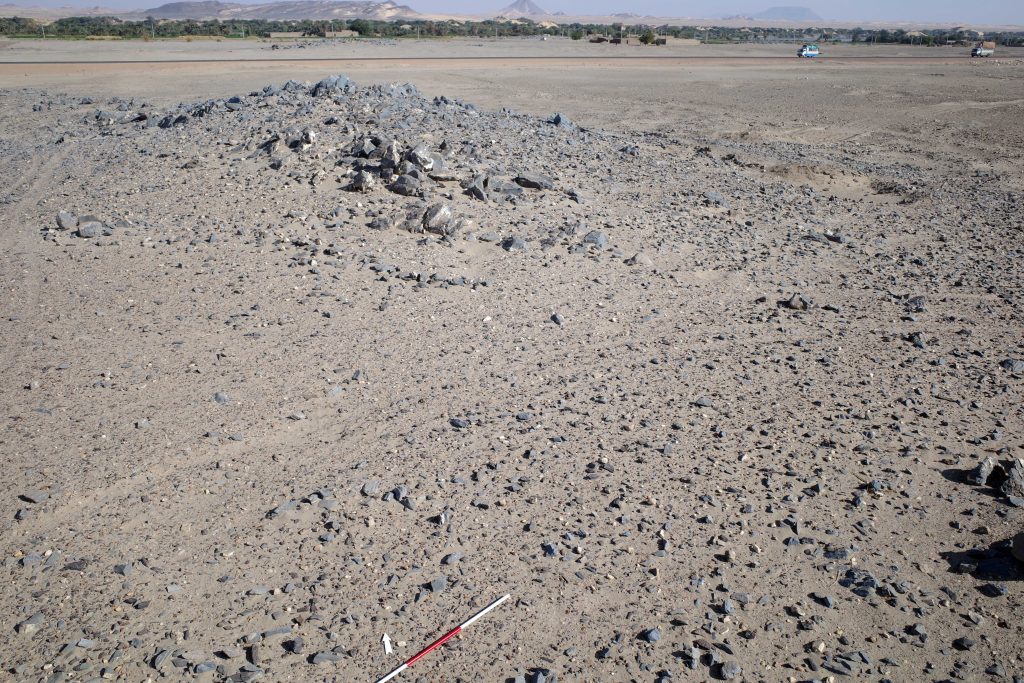
Vila documented two sites on the island – the better preserved one is 2-S-21, a fortified village of 110 x 70m in size which Vila associated with the Terminal Medieval period (Vila 1977: 32-37) in the southwestern corner of the island. He provided an excellent map of the site, and we could follow in his footsteps and check the present day preservation.
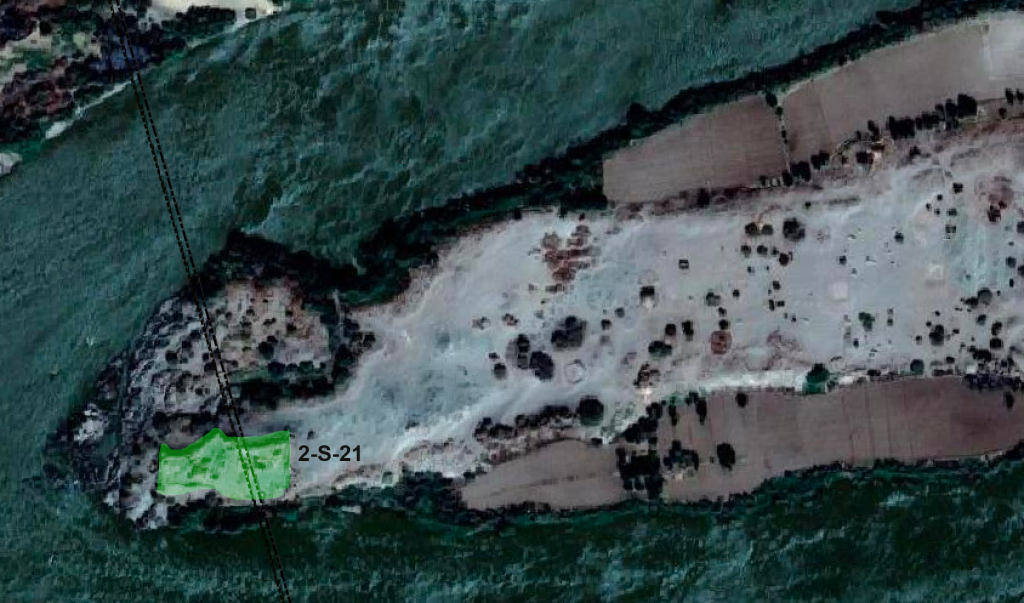

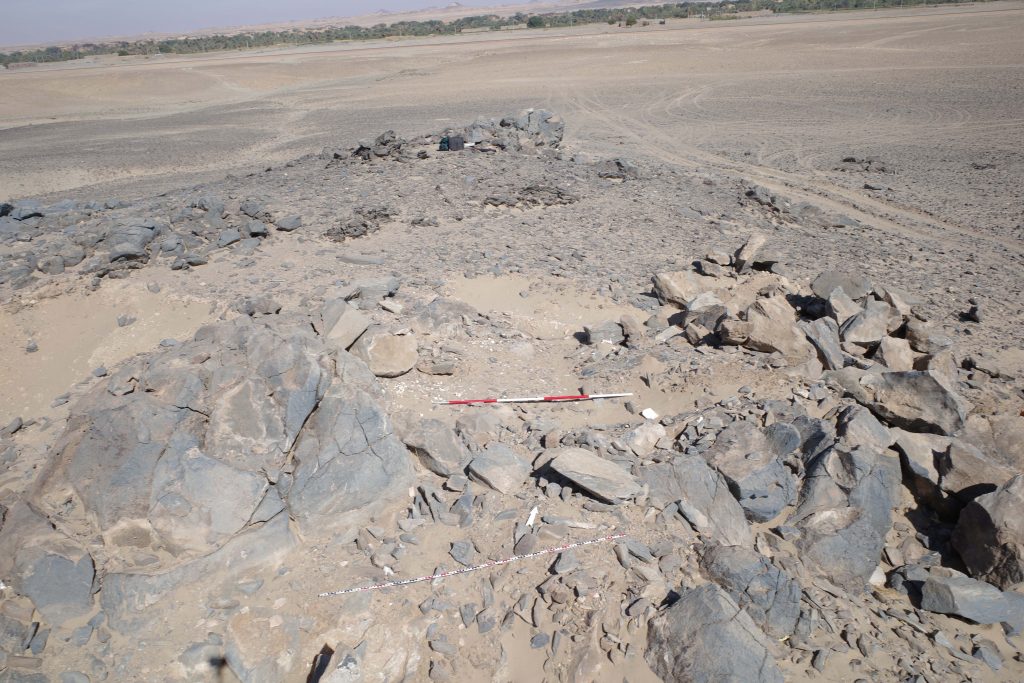
The enclosure wall has a hexagon shape and is made of mud brick with blocks and pieces of schist stone. In the southern part, the enclosure has already partly collapsed in the times of Vila, but the buildings in the interior are still very well preserved.
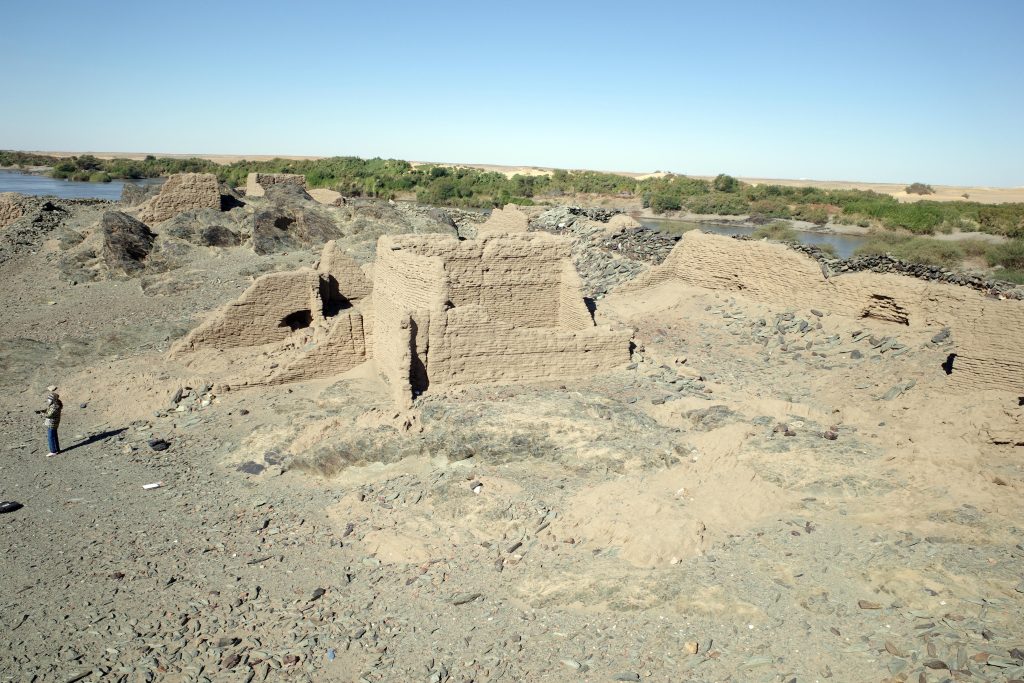
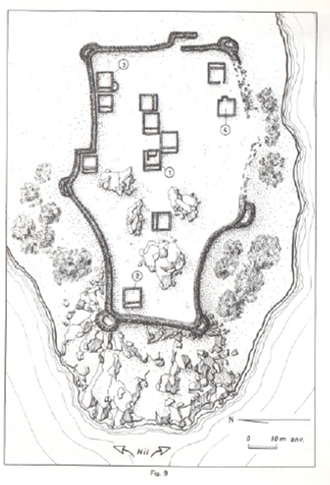

A dozen of preserved mud brick houses are square or rectangular buildings with one very small room in the back and a larger room in the front. Such a layout as well as the general appearance of the settlement 2-S-21 seems typical of the Funj period. Much progress in research on Funj house architecture has just been made in the last years, most prominently by the UMMA project at Old Dongola. In one of their recent publications, Obłuski and Dzierzbicka point out the main characteristics and differences to the medieval Nubian house types. They also mentioned Gergetti island as a close parallel to Old Dongola (Obłuski & Dzierzbicka 2021, 237, 242).
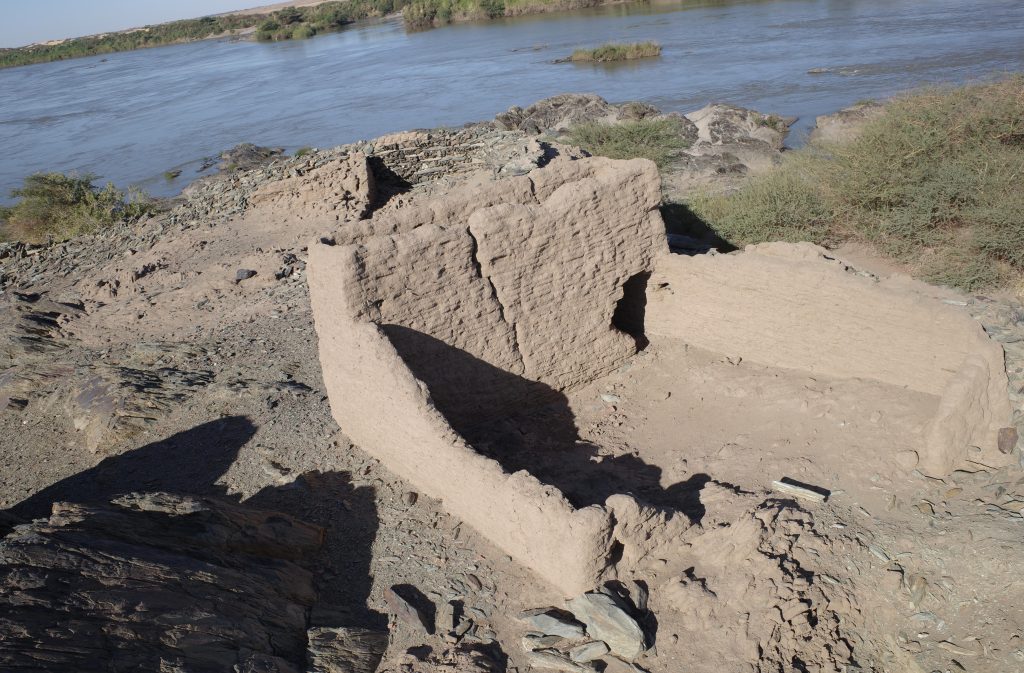

Especially since research of Funj period domestic architecture between the Second and Third Cataracts is still limited, the site 2-S-21 has much potential for future exploration. It became obvious that the map of Vila, as useful as it is, needs to be improved in several respects and that some buildings were also omitted on his plan. One possibility would be to document the site by drone aerial photography and thus to generate a new georeferenced 3D model as well as detailled plans. Excavations should also be undertaken in selected parts of the town, especially for clarifying building phases. The earliest phase of the settlement would be extremely relevant – not only for further comparisons with Old Dongola and other sites, but also from a historical view for the region of Attab to Ferka. Apart from the architecture, the material culture will give important information on the fine dating (as well as on so many other questions like room function, activities etc.). There is plenty of pottery on the surface, including nice painted wares and we also found one small piece of glazed ware. Without doubt, undisturbed contexts more useful for dating can be expected below some of the collapsed walls.
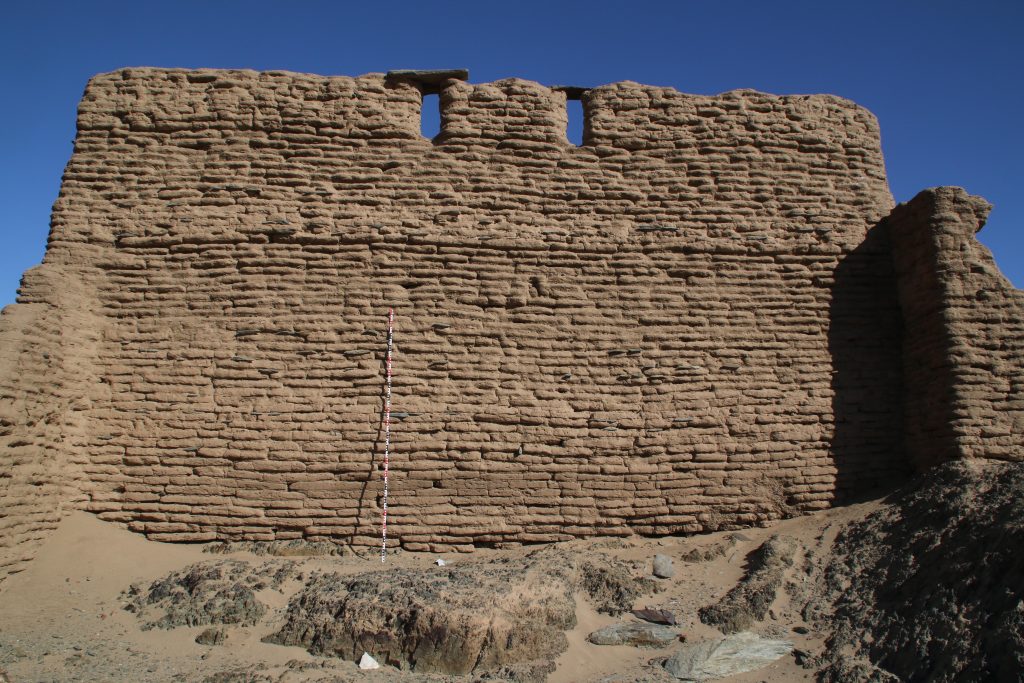

For now, Vila’s association of the site with Late Medieval times should be modified as most likely Funj period – more on this will follow when we return to the beautiful island of Gergetti.
References
Obłuski, A. and Dzierzbicka, D. (eds) 2021. Old Dongola: development, heritage, archaeology. Fieldwork in 2018-2019. Volume 1: Excavations. Polish Publications in Mediterranean Archaeology 1. Leuven et al.
Vila, A. 1977. La prospection archéologique de la Vallée du Nil, au Sud de la Cataracte de Dal (Nubie Sudanaise). Fascicule 6: Le district de Attab, Est et Ouest. Paris: CNRS.